Muscle Contusions
Muscle contusions (bruise) are common in athletes but also in everyday people. In fact, are the second most common cause of sports injuries. Contusions typically heal quickly without forcing the athlete to take extensive time off. However, severe contusions can cause deep tissue damage and keep them out of the game for months.
Causes
Contusions occur after a blow from a blunt object strikes the body and crushes the muscle fibers and connective tissue without breaking the skin. A contusion can happen from falling or pushing against a hard surface. A contusion can be as traumatic and painful as a tear or break (fracture); however, they are often underestimated since they can’t be seen.
Symptoms
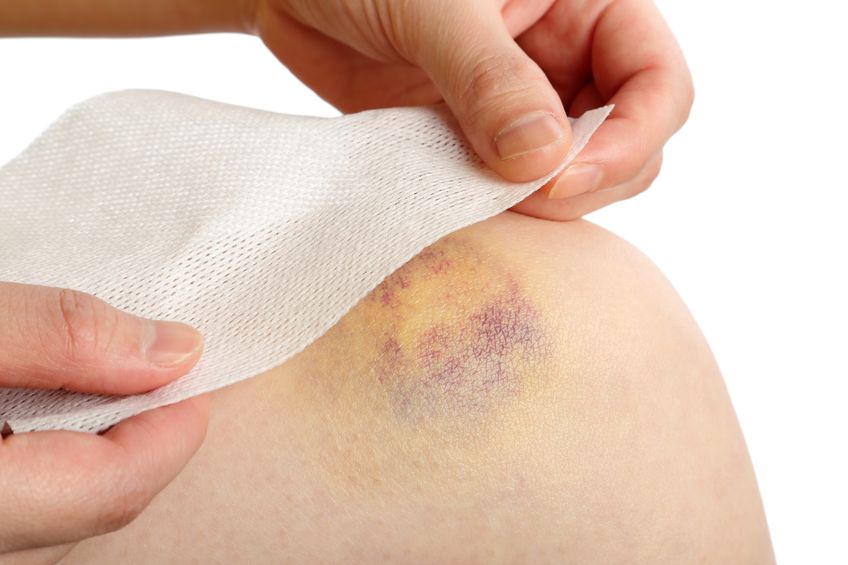
Contusions are known to cause swelling and pain near the area of injury. Damaged blood vessels result in a bluish discoloration. A pool of blood can collect within the damaged tissue and form a bump. The muscle may feel weak, stiff and sore days after the injury is incurred. If damage is extensive a broken bone, sprain, tear or other injury may also be present. Contusions of the abdomen may damage internal organs. Contusions in superficial locations, such as the shin (tibia) or elbow can have blue, black, brown and yellow discolorations for weeks.
Treatment
The RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) formula can be applied to the contusion. Some doctors may recommend an non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug like ibuprofen. The first 24 to 48 hours after the injury RICE will be the best method to employ for relief. If a large hematoma doesn’t disappear within a few days a doctor may need to drain it surgically. Compression marments are extremely effective to treat contusions.
Recovery
Within a few days the inflammation should start to go down and the injury should feel less painful. A doctor may recommend gentle heat to the injury at this point. Activity levels can be increased gradually. Returning to sports or everyday activities may take several weeks. Putting too much stress on the area before it has healed can lead to scar tissue and more problems. A doctor may recommend gentle stretching exercises to restore range of motion. Weight bearing and resistance exercises should be considered after range of motion has improved. Physical therapy is an excellent treatment for contusion; a professional therapist can optimize the muscles recovery and function.
Complications
Compartment syndrome and Myositis Ossificans can occur in serious cases. Compartment Syndrome may require surgery to drain excessive fluids and swelling to the muscle. This is a serious condition that usually causes extreme pain. Immediate attention is required. The condition is caused by rapid bleeding, a build up of fluid, and can disrupt blood flow. Myositis Ossificans is a condition in which the bruised muscle grows bone instead of new muscle cells. RICE can help this condition and improve flexibility; surgery isn’t usually required. Myositis ossifican is common in the thighs of football players; however now all uniforms have padding on the front of the legs.
For more information on Muscle Contusions visit the American Society of Orthopaedic Surgeons.




