How To Treat One Of The Most Common Causes Of Knee Pain: A Torn Meniscus.
Treating a Torn Meniscus
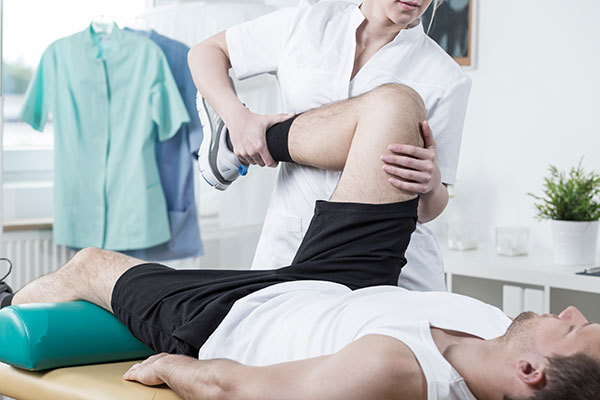

The good news about meniscal tears is that most of them may be treated without surgery. Physical therapy along with proper bracing is often successful. Occasionally, injections into the knee may be used for pain relief, growth, or to promote healing in order to avoid surgery.
Physical Therapy
A well trained physical therapist that is attentive to your particular type of tear and overall condition is a safe and effective way to treat a lot of these tears. A good therapist should:- Check the hips, ankle and lower back for deficiencies
- Assess the knee’s flexibility and strength – these must be addressed. The muscles that cross the knee act as shock absorbers and if properly strengthened and conditioned can protect a meniscal tear while it heals.
- The therapist may use advanced techniques such as dry needling and manual stimulation of the muscles.
- A manual physical therapist (a special and highly trained designation) will be able to manipulate the knee, hip and ankle joints as well as the spine as needed to improve the overall leg function.

Surgical Options
Surgery for a torn meniscus is very common in the U.S. Although it is always important to avoid surgery if possible, sometimes there is no other option for treating a torn meniscus. Surgery for a meniscal tear is usually done arthroscopically, meaning that a small camera and another small tool are inserted into the knee. A surgeon is able to see inside the knee with the fiber optic camera. Surgery for a torn meniscus is typically a simple removal of the torn portion, keeping as much healthy meniscus intact and inside the knee as possible.
After surgery, physical therapy is very important, as is bracing and possible injections of healing substances. Usually therapy will start within a week after surgery and continue for 4-6 weeks, during which one or two visits with the therapist per week is usually adequate. Therapy is important to strength the muscles around the knee and to maintain the appropriate flexibility of the knee tissues. If your knee gets weak and stiff after a meniscal surgery, the surgery will not work to reduce pain. Rehabilitation after surgery is as important as the surgery itself.
Medications will include pain medicines and supplements devised to promote healing. It is important for overweight patients to lose weight to aid the healing process, as each extra pound above the waist is felt as 4-5 pounds by the knee. If the orthopedic surgeon selects a proper brace, the meniscus and cartilage can remain protected even during contact sports.